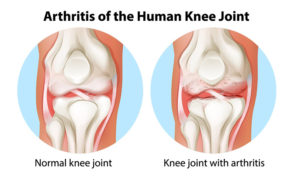
Osteoarthritis usually develops after years of use. It is common in the knees because the knees bear the weight of the body. Over time, the cartilage in the knee wears down and stops protecting the ends of bones in the joint.
Causes and risk factors
- Wear and tear of aging
- Traumatic injury to the joint
- Developmental dysplasia
- Inflammatory arthritis
- Osteonecrosis
- Infection
- Metabolic disorders
- Hemoglobinopathies and other blood disorders
- Autoimmune disorders
- Obesity
Symptoms
- Pain, swelling, and stiffness
- The knee may lock or buckle when walking
- Trouble bending or straightening the knee
- Standing or walking for long periods may worsen pain
Diagnosis and treatment
Nonoperative treatment options include injections, physical therapy, taking anti-inflammatories, activity modification, weight loss, bracing, and using a cane/walker. If these are not helpful, an orthopedic surgeon may recommend surgery such as total knee replacement (knee arthroplasty) to relieve pain and preserve mobility.